Contrast Effects
Posted on 06/28/2012
A contrast effect in color theory is the impact that one color has on the perception of another color.
A common example of a contrast effect is a "simultaneous contrast" in which two colors are observed at the same time. This is best understood through the following graphic illustration*.
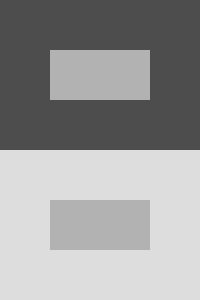
In this illustration, the inner gray rectangles are identical colors. However, the inner gray rectangle appears lighter when viewed against the darker background, and darker when viewed against the lighter background.
This visual phenomenon has a direct impact on tooth shade selection in dentistry. For example, a tooth viewed against a dark gingiva will appear lighter than a tooth viewed against a lighter gingiva.
For the purpose of our discussion of contrast effects in clinical settings, we will delineate contrast effects in the following six categories:
1. Hue
2. Value
3. Chroma
4. Areal
5. Spatial
6. Successive
*Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Contrast_effect
Portions of this post were adapted from the book:
Fundaments of Color - Shade Matching and Communication in Esthetic Dentistry published by Quintessence Publishing Co. Inc
and the
Wikipedia article/s:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Contrast_effect
A common example of a contrast effect is a "simultaneous contrast" in which two colors are observed at the same time. This is best understood through the following graphic illustration*.

In this illustration, the inner gray rectangles are identical colors. However, the inner gray rectangle appears lighter when viewed against the darker background, and darker when viewed against the lighter background.
This visual phenomenon has a direct impact on tooth shade selection in dentistry. For example, a tooth viewed against a dark gingiva will appear lighter than a tooth viewed against a lighter gingiva.
For the purpose of our discussion of contrast effects in clinical settings, we will delineate contrast effects in the following six categories:
1. Hue
2. Value
3. Chroma
4. Areal
5. Spatial
6. Successive
*Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Contrast_effect
Portions of this post were adapted from the book:
Fundaments of Color - Shade Matching and Communication in Esthetic Dentistry published by Quintessence Publishing Co. Inc
and the
Wikipedia article/s:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Contrast_effect
Contrast Effects, Simultaneous contrast, Hue, Value, Chroma, Color in dentistry, shade selection, dentist, dental lab tech
- Simultaneous Contrast : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Contrast_effect










